The level of maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max) describes the highest amount of oxygen that human body is able to consume during one minute and is usually expressed in absolute (Liters/min) and relative (mL/kg/min) units.
According to the scientific literature, the major factors that determine the level of VO2max are:
- the ability of cardio-vascular system to transport oxygen to working muscles
- ability of oxygen utilization in the muscles (in the mitochondria)
The measurements of VO2max involve laboratory exercise tests (usually on mechanical treadmills or cycle ergometers) with progressively increasing intensity, during which a basic criterion of reaching VO2max is the oxygen uptake stabilization despite of further load increases. The exercise during laboratory test should be similar to the specificity of the athlete’s sports discipline (i.e. cycle ergometry for cyclists and treadmill running for runners).
According to Fick’s law, VO2max is equal to the product of the maximum heart rate (HRmax), stroke volume (SV) and the arterio-venous oxygen difference (CaO2 – CvO2):
VO2max = HRmax x SV x (CaO2 – CvO2)
The measurement of cardiac stroke volume and arterio-venous oxygen difference requires the use of invasive diagnostic methods and therefore because of practical and ethical reasons it is not used during standard exercise tests. Nevertheless, oxygen uptake may also be assessed on the basis of an analysis of the changes of ventilation indices (minute ventilation of lungs and oxygen and carbon dioxide contents in inspired and expired air).
It is worth to mention that the main cardiac parameter affecting the level of VO2max, is the cardiac output (CO) – the amount of blood the heart pumps during 1 minute (CO = HR x SV). The maximum heart rate during intensive exercise is relatively constant, regardless of the level of aerobic fitness. In well-trained athletes a left ventricular hypertrophy of the heart causes an increase in stroke volume (SV) (the amount of blood the heart pumps during one contraction). In untrained person stroke volume during exercise is approximately 120-130 mL of blood per stroke compared to trained athlete whose stroke volume is about 160-200 mL.
The resting cardiac output is about 5 L/min in both trained and untrained, but during a maximum effort in a healthy untrained man it rises up to about 20 L/min and in highly trained endurance athletes cardiac output rises even up to 40 L/min.
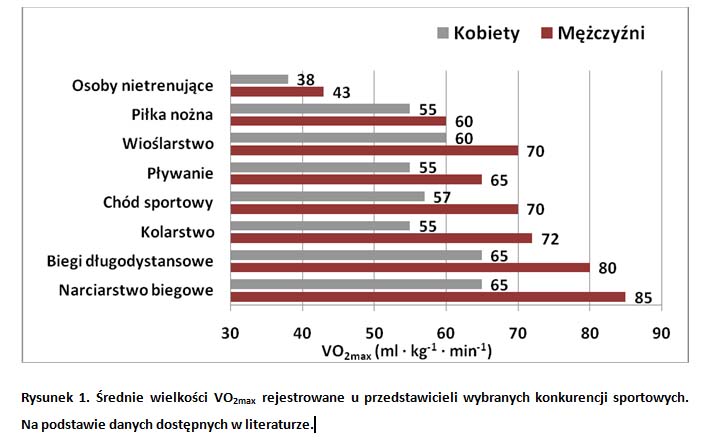
A very high levels of VO2max that are observed in medium and long-distance runners, are determined by genetic factors (approximately 40%) and by training (in 5-30%). In fig. 1 typical levels of VO2max of top class athletes are presented.
The activity of intensity at the level of VO2max can only be continued for just a few minutes. In the case of top level runners, the running speed at the intensity corresponding to VO2max may be useful in predicting the possible results in running events ranging from 1500 to 5000 meters.
The scientific studies on the athletes reveal that the energy demands of long distance events, such as: 1500m, 3000m, 5000m and 10000m correspond to: ≈ 110, 100, 96 and 92% of VO2max, respectively. As the duration of activity and distance increases, the importance of VO2max decreases and the importance of other aerobic fitness indices increases, such as lactate threshold and running economy.
Based on:
Whyte G., (editor). The Physiology of Training. Advances in Sport and Exercise Science Series. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, 2006.